Hubble Captures Stunning Dark Matter Web in Galaxy Cluster

Hubble Reveals Dark Matter Web in Abell 209 Galaxy Cluster
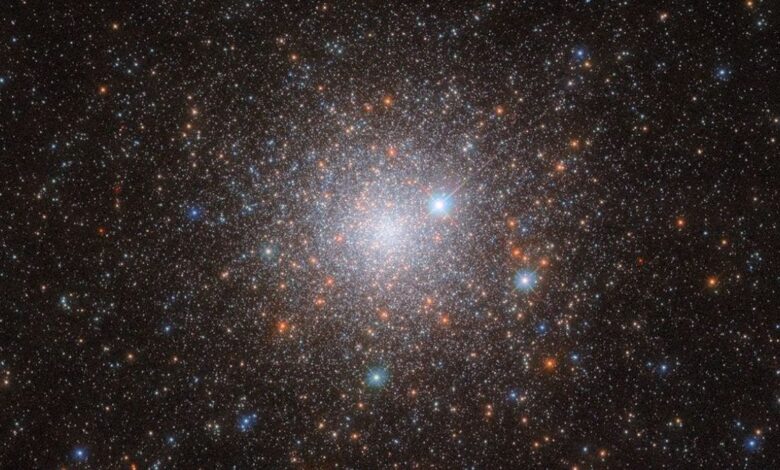
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured an awe-inspiring image of Abell 209, a massive galaxy cluster located 2.8 billion light-years away in the constellation Cetus. This cluster, a cosmic metropolis, is home to over 100 galaxies bound together by the relentless pull of gravity. However, the visible galaxies are only part of the story. A vast, unseen network of hot, diffuse gas and dark matter permeates the cluster, shaping the universe through its gravitational influence. Hubble’s powerful lenses allow scientists to probe these invisible components and the warped spacetime they create.
Unveiling the Invisible Universe
Dark matter, an enigmatic substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe’s mass, doesn’t interact with light, rendering it invisible to conventional telescopes. Its presence is inferred through its gravitational effects on visible matter, such as the bending of light from distant galaxies. This phenomenon, known as gravitational lensing, provides a unique window into the distribution of dark matter within galaxy clusters like Abell 209.
Hubble’s Technological Prowess
The stunning image of Abell 209 was captured using Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). Twelve exposures taken through various color filters were meticulously combined to create the final, breathtaking view. The image showcases a golden glow emanating from numerous bright elliptical galaxies concentrated at the cluster’s center, contrasted by the faint blue hues of spiral galaxies scattered along the edges. By operating above Earth’s atmosphere, Hubble circumvents atmospheric blurring, revealing distant galaxies with exceptional clarity.
Optical and Infrared Synergy
Hubble’s technological brilliance is evident in its ability to merge optical and infrared data into a single, striking cosmic portrait. Visible light reveals the smooth, golden orbs of the largest galaxies, while infrared light penetrates dust clouds, unveiling hidden structures and details. This synergy provides a more complete and nuanced understanding of the galaxy cluster and its constituents.
Scientific Implications and Discoveries
Images like the one of Abell 209 are invaluable for addressing fundamental questions about dark matter and dark energy, the mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe. The space between Abell 209’s galaxies is filled with X-ray-emitting hot gas and dominated by dark matter. Ordinary matter, the stuff that makes up stars, planets, and us, accounts for only about 5% of the cosmos. Dark matter comprises roughly 25%, while dark energy makes up the remaining 70%.
Gravitational Lensing: A Cosmic Magnifying Glass
A massive galaxy cluster acts as a natural lens, its immense gravity warping the light from galaxies located far behind it. In the Hubble image of Abell 209, faint background galaxies appear stretched into curved streaks. By precisely measuring these distortions, scientists can map the cluster’s total mass distribution, including the elusive dark matter. This allows them to test and refine theories about how the universe has evolved under the influence of dark matter and dark energy.
Exploring the Universe’s Evolution
- Understanding the distribution and properties of dark matter is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of galaxy formation and the large-scale structure of the universe.
- By studying galaxy clusters like Abell 209, astronomers can gain insights into the processes that have shaped the cosmos over billions of years.
- The ongoing observations and analysis of these cosmic structures promise to further illuminate the nature of dark matter and dark energy, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe.
Key Findings:
| Element | Percentage | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary Matter | 5% | Forms stars, planets, and all visible objects. |
| Dark Matter | 25% | Influences gravity and shapes the structure of the universe. |
| Dark Energy | 70% | Drives the accelerated expansion of the universe. |