Rare Aurora Over Ladakh: Indian Scientists Solve Mystery
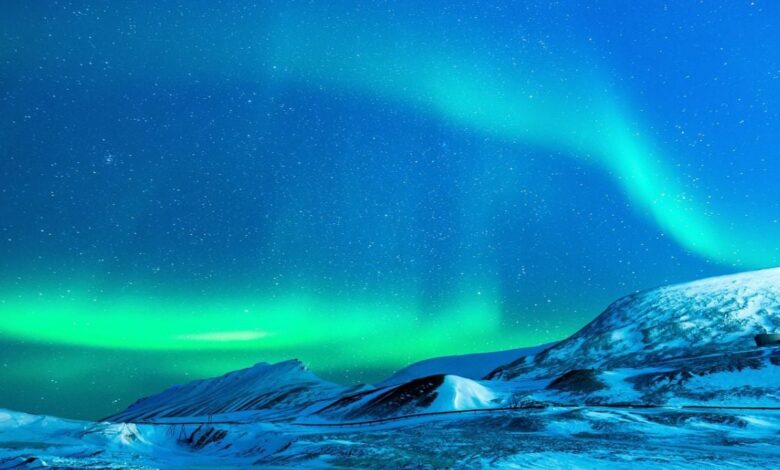

Rare Aurora Lights Up Ladakh: A Scientific Breakthrough
On May 10, 2024, the skies above a remote village in Ladakh erupted in a dazzling display of red and green auroras, a phenomenon unseen in the region for over a decade. This extraordinary event was triggered by a powerful solar storm, specifically Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), which are magnetized plasma ejections hurled from the Sun at speeds reaching millions of kilometers per hour. These eruptions, often caused by filament eruptions and solar flares, send massive amounts of energy toward our planet, sometimes resulting in the mesmerizing spectacle of auroras.
The Fiery Solar Storm and its Impact
The recent auroral display was ignited by an intense solar storm, prompting immediate investigation by Indian scientists. The rarity of such an event in this southern latitude made it a particularly compelling subject of study. Auroras, typically observed closer to the Earth’s poles, occur when charged particles from the sun interact with the Earth’s magnetic field, exciting atmospheric gases and causing them to glow.
Indian Scientists Investigate the Auroral Phenomenon
A team of Indian scientists, led by Dr. Wageesh Mishra, embarked on a mission to understand the underlying causes of this rare auroral event. Utilizing data from NASA, ESA, and various ground-based facilities, the team focused their analysis on observations from the Indian Astronomical Observatory. They employed the Flux Rope Internal State (FRIS) model to enhance coronagraph images and meticulously map the evolving temperature, magnetic fields, and structure of the CMEs as they journeyed through interplanetary space.
Mapping CME Thermal Dynamics
This research marks the first global study to comprehensively chronicle the thermal dynamics of CMEs from the Sun to Earth. Their findings have been published in the prestigious journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, highlighting the significance of this scientific endeavor.
Unexpected Reheating of Coronal Mass Ejections
One of the most surprising discoveries was the unexpected reheating of the CMEs. Contrary to previous assumptions that these ejections would cool as they expanded, the scientists observed that they actually heated up midway through their journey. This reheating phenomenon maintained a relatively constant temperature until the CMEs impacted Earth. The thermal restructuring is attributed to the collision of two CMEs, where electrons release high temperatures, and ions release a mix of lower and higher temperatures.
Magnetic Collision and the Triggering of Auroral Lights
Data obtained from NASA’s Wind Spacecraft provided crucial insights into the interaction between the solar storm and Earth’s magnetosphere. The data revealed that the plasma enveloped Earth in double flux ropes – twisted magnetic structures capable of triggering significant geomagnetic disturbances. This complex magnetic entanglement is what allowed the auroras to extend as far south as Ladakh, creating a spectacular light show witnessed by local residents.
Double Flux Ropes Explained
Double flux ropes can be visualized as intertwined magnetic field lines that act as conduits for energy and charged particles. When these structures interact with Earth’s magnetic field, they can cause significant disturbances, leading to auroras and other space weather phenomena.
Global Implications and a Research Breakthrough
This research holds significant implications for global space weather forecasting and enhances India’s capabilities in this critical area. By gaining a deeper understanding of the thermal and magnetic changes within CMEs, scientists can improve early-warning systems for potential disruptions to power grids, navigation systems, and satellite operations.
Enhancing Space Weather Forecasting
Accurate space weather forecasting is essential for mitigating the risks associated with solar storms. These events can have a significant impact on our technologically advanced society, disrupting communication networks, causing power outages, and endangering astronauts in space.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Coronal Mass Ejections | Large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. |
| Auroras | Natural light displays in the sky, predominantly seen in the high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). |
| Flux Ropes | Twisted magnetic structures in space that can carry large amounts of energy and charged particles. |
| Space Weather | The conditions in space that can affect Earth and its technological systems. |
The Future of Space Weather Research
This groundbreaking research paves the way for future investigations into the complex dynamics of solar storms and their impact on our planet. By continuing to unravel the mysteries of space weather, scientists can better protect our infrastructure and ensure the safety of our increasingly interconnected world.