Spectacular Solar Filament Eruption Creates ‘Canyon of Fire’
Sun Erupts: Massive Solar Filament Creates ‘Canyon of Fire’
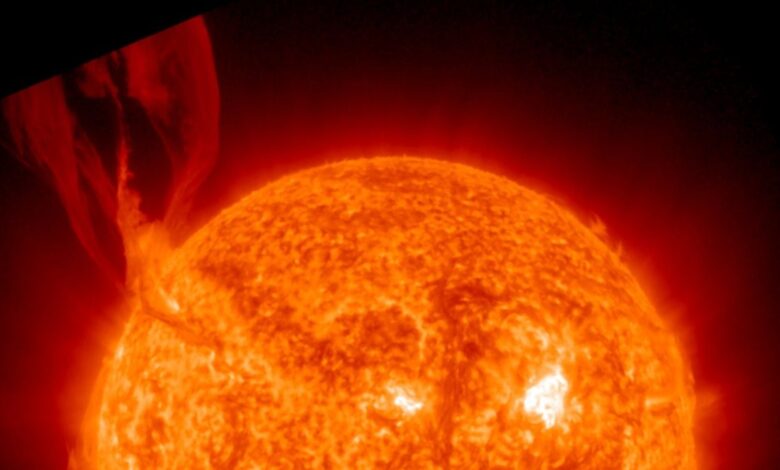
On July 15th, a colossal solar filament eruption occurred on the sun’s northeastern limb, resulting in a spectacular display of solar activity. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured high-definition video of the event, revealing a bright chunk of solar material ejected hundreds of thousands of miles into space – approximately a quarter of the distance between the Earth and the Moon. This event sculpted a 250,000-mile-long “canyon of fire” on the sun’s surface.
The eruption involved towering walls of plasma, reaching over 12,400 miles in height and spanning more than three times that width. This dynamic rearrangement of the sun’s magnetic field created a breathtaking visual spectacle.
What are Solar Filaments?
Solar filaments are cooler, denser clouds of solar material suspended above the sun’s surface by magnetic forces. They appear as dark, thread-like structures when viewed against the sun’s bright disk. When these magnetic structures become unstable, they can collapse, leading to eruptions and the release of energy.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) and Space Weather
Often, solar filament eruptions are associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs). CMEs are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. These ejections can travel outward into space at high speeds, potentially interacting with planetary magnetic fields, including Earth’s.
CME from July 15th Eruption
The July 15th eruption did produce a CME. However, initial observations indicated that it was not directed toward Earth. Data from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and the GOES-19 satellite confirmed that the CME’s trajectory was away from our planet.
The Science Behind the Spectacle
According to SpaceWeather.com, the “canyon of fire” observed after the eruption was a consequence of magnetic field lines snapping and reconnecting violently. This process leaves behind a trail of superheated plasma, creating the glowing rift.
- Magnetic reconnection is a fundamental process in plasma physics where magnetic field lines break and reconnect, releasing energy in the process.
- This energy release can accelerate particles to high speeds and heat the surrounding plasma.
Implications for Space Weather Forecasting
While the CME from this particular eruption did not pose a direct threat to Earth, understanding these events is crucial for space weather forecasting. Solar filament eruptions and associated CMEs are fundamental drivers of space weather, which can impact satellite operations, communication systems, and even power grids on Earth.
- Monitoring solar activity allows scientists to predict potential disruptions to our technological infrastructure.
- Improved forecasting can help mitigate the risks associated with space weather events.
Observing the Dynamic Sun
The video of the July 15th eruption serves as a powerful reminder of the dynamic and sometimes explosive nature of the sun. It provides a glimpse into the immense forces at play on our star and their potential impact on the solar system.
Scientists continue to study these events to better understand the underlying physics and improve our ability to predict future space weather events.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Solar Filament | A cooler, denser cloud of plasma suspended above the Sun’s surface by magnetic fields. |
| Filament Eruption | The sudden release of a solar filament, often accompanied by a coronal mass ejection (CME). |
| Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) | A large expulsion of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. |
| Magnetic Reconnection | A process where magnetic field lines break and reconnect, releasing energy. |
| Space Weather | The conditions in space that can affect Earth and its technological systems. |
Further Research
Scientists are continuously observing the Sun to understand these events better. Advanced instruments and observatories like SDO and SOHO provide valuable data for studying solar activity and improving our understanding of space weather.